You are at the centre of our everyday efforts and you encourage us to give our very best in creating medical solutions.
Products
 Creating with you in mind starts by listening to you, identifying your unmet needs and utilising our expertise and passion to provide and supplying highly safe , effective and easy -to -use skin treatments and the best choices of internationally wound healing products .
Creating with you in mind starts by listening to you, identifying your unmet needs and utilising our expertise and passion to provide and supplying highly safe , effective and easy -to -use skin treatments and the best choices of internationally wound healing products .
Disease Awareness
Understanding a disease plays a key role in the ability to cope with it, to find the right treatment or eventually overcoming it. Sometimes, understanding a disease can also help to prevent it. The following information aims to improve your health through empowerment with everything you need to know.
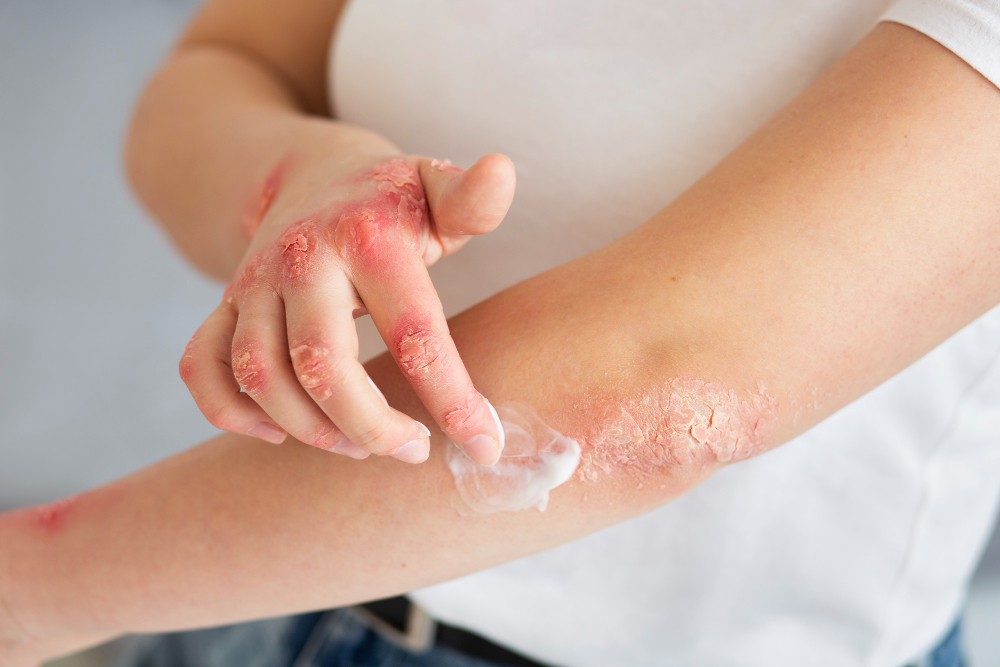
What causes skin diseases?
Certain lifestyle factors can lead to the development of a skin disease. Underlying health conditions may affect your skin, too. Common causes of skin diseases include:
Creating with you in mind starts by listening to you, identifying your unmet needs and utilising our expertise and passion to provide and supplying highly safe , effective and easy -to -use skin treatments and the best choices of internationally wound healing products .
- Bacteria trapped in your pores or hair follicles.
- Conditions that affect your thyroid, kidneys or immune system.
- Conditions that affect your thyroid, kidneys or immune system.
- Contact with environmental triggers, such as allergens or another person’s skin.
- Genetics
- Fungus or parasites living on your skin.
- Medications, such as the ones that treat inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Viruses.
- Diabetes.
- Sun.
How is a skin disease diagnosed?
Often, a healthcare provider can diagnose a skin disease by visually examining your skin. If looking at your skin doesn’t provide clear answers, your provider may use tests such as:
- Biopsy, removing a small piece of skin to examine under a microscope.
- Culture, taking a skin sample to test for bacteria, fungus or viruses.
- Skin patch test, applying small amounts of substances to test for allergic reactions.
- Black light examination (Wood light test), using an ultraviolet (UV) light to view your skin’s pigment more clearly.
- Diascopy, pressing a microscope slide against a skin patch to see if the skin changes color.
- Dermoscopy, using a hand-held device called a dermatoscope to diagnose skin lesions.
- Tzanck test, examining the fluid from a blister to check for herpes simplex or herpes zoster.
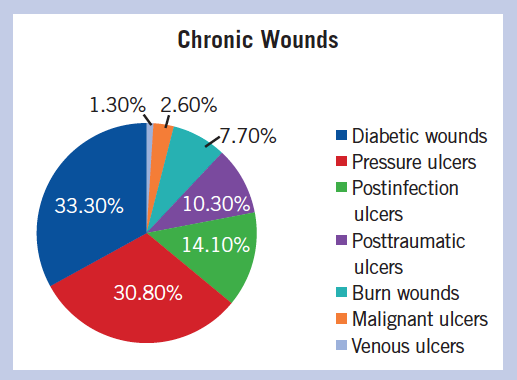
Types of Wounds
Persistent non-healing wounds come in many forms. Depending on the type of wound your physician will prescribe a different course of treatment. Some wounds, such as pressure sores, diabetic ulcers, and vascular ulcers may require surgical debridement, which is the removal of weakened or dead tissue. Reconstructive surgery is also a possibility for wound repair.

Diabetic Wounds
Diabetic wounds and ulcers often occur on lower extremities and are frequently associated with diabetic neuropathy also known as a decrease in sensation. Diabetic ulcers can be quite severe and sometimes lead to surgical amputation. Diabetic wounds often require management by more than one physician. A surgeon will work in conjunction with your care team if surgery to remove or reconstruct the wound is necessary.
Neoplastic Wounds
Skin and soft tissue cancers related to chronic wounds are a frequently under-recognized cause of non-healing. The appearance of a cancerous wound can be fairly unexceptional; as such chronic non-healing wounds that have not responded to traditional wound care regimens benefit from assessment by a wound specialist. The wound care specialist may biopsy, or sample, the soft tissue of the wound for further analysis.
Pressure Ulcers
Pressure ulcers develop when external pressure over a bony area cuts off the supply of oxygen and nutrients to soft tissue like skin or muscle. This results in tissue damage. Over time, issues can range from treatable wounds to outright death of the tissue.
The skin is more tolerant of pressure than the underlying fat and muscle. Pressure-related skin changes are the “tip of the iceberg” compared with the extent of the underlying tissue damage. Common locations for pressure ulcers can be the lower back, tail bone, buttocks, heels, back of the head, and the sitting bones.
Radiation Related Wounds
Radiation-induced tissue injury is a common side-effect of radiation therapy. Tissue changes can occur suddenly or long after therapy is completed and usually appears at the site of treatment but can also appear in the soft tissue nearby.
Radiation related wounds can also develop because of minor trauma to the radiated tissue. Surgical incisions located on or near radiated tissue may have difficulty closing, resulting in non-healing wound.
For some patients, hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) can be prescribed in addition to conventional medical and surgical care for radiation related tissue injury.
Vascular Wounds
Vascular ulcers are wounds which usually occur below the knee as a result of a decreased blood flow and can affect one or both legs. Vascular ulcers are common in patients who have a history of swelling in their legs, varicose veins, or blood clots. Like diabetic ulcers, management usually requires more than one doctor – for example, a surgeon will work together with a patient's care team if surgery is required.
"We believe biotech innovations can help to build a more secure life for all of us. We want to improve the quality of life of people suffering from any wound type by providing safe, effective & easy-to-use skin & wound healing solutions."